Website Backup Guide
Regular backups are essential for website security and recovery. This guide covers backup strategies and step-by-step instructions for backing up your website files and databases using common hosting tools.
Regular backups are essential for website security and recovery. This guide covers backup strategies and step-by-step instructions for backing up your website files and databases using common hosting tools.
A complete website backup consists of two components: your website files and your database (for dynamic sites like WordPress). Both are essential for fully restoring your site if problems occur.
Once your website is launched, create an initial backup to preserve the original version. This serves as your baseline that you can always return to if needed.
Establish a regular backup routine based on how frequently your site changes:
Follow this best practice for backup redundancy:
Use clear naming for easy identification: sitename_YYYY-MM-DD_type
Example: mywebsite_2025-01-15_full.zip
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) provides direct access to download your website files. This method works with any hosting provider.
FileZilla – Free, reliable, and cross-platform FTP client
→ Download from: https://filezilla-project.org/
Note: Download the “Client” version, not “Server”
Once connected, you’ll see two panels:
To backup your website:
cPanel provides built-in backup tools that are faster and more convenient than FTP for most users.
Login to cPanel using one of these methods:
yourdomain.com/cpanelOnce logged in, locate and click the “Backup Wizard” icon:
Step 1: Choose Backup Type
Select “Backup” (not Restore) from the main screen:
Step 2: Select Partial Backup
Choose from the “Partial Backup” options on the right:
Note: Avoid “Full Backup” – it’s for server migrations, not regular backups
Step 3: Download Your Backups
Click each item to download. Files will save to your Downloads folder.
For large sites or slow servers, using File Manager can be more efficient:
To restore your backups:
phpMyAdmin is the standard tool for database management and is available on most hosting platforms.
In cPanel, find and click the phpMyAdmin icon:
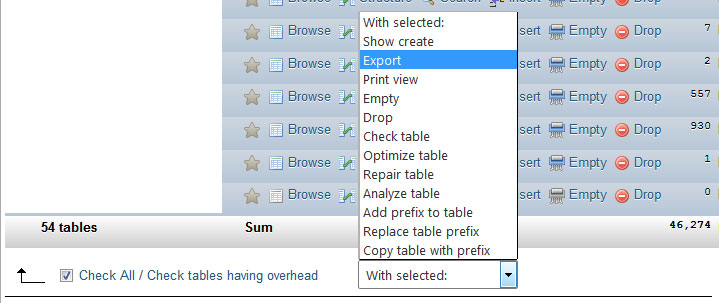
On the export screen, use these recommended settings:
To restore a database backup:
Note: For large databases, you may need to:
For detailed database restoration instructions, see: Database Backup Guide
WordPress sites require special attention due to their dynamic nature and frequent updates.
A complete WordPress backup includes:
Platform Updates (WordPress core):
Plugin Updates:
Theme Updates:
While manual backups are important, these plugins can automate the process:
Recommended Free Plugins:
Premium Solutions:
Test your backup recovery process before you need it:
Solutions to frequent backup problems and error messages.
Problem: Backup file too large to download or upload
Solutions:
Problem: Backup process times out before completion
Solutions:
Problem: Database won’t import or shows errors
Solutions:
Problem: Backup files won’t extract or are damaged
Prevention:
Problem: Running out of space for backups
Solutions:
Problem: Can’t create or access backup files
Solutions:
Regular backups are your insurance policy against data loss, hacking, and update failures. If you need help setting up an automated backup system, recovering from a failed update, or implementing a comprehensive backup strategy, please don’t hesitate to reach out. Remember: it’s not a matter of if you’ll need a backup, but when.